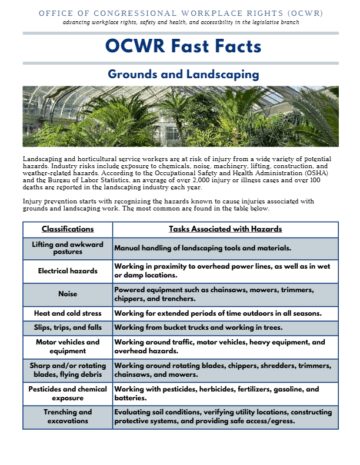
Landscaping and horticultural service workers are at risk of injury from a wide variety of potential hazards. Industry risks include exposure to chemicals, noise, machinery, lifting, construction, and weather-related hazards. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the Bureau of Labor Statistics, an average of over 2,000 injury or illness cases and over 100 deaths are reported in the landscaping industry each year.
Injury prevention starts with recognizing the hazards known to cause injuries associated with grounds and landscaping work. The most common are found in the table below.
| Classifications | Task Associated with Hazards |
| Lifting and awkward postures | Manual handling of landscaping tools and materials. |
| Electrical hazards | Working in proximity to overhead power lines, as well as in wet or damp locations. |
| Noise | Powered equipment such as chainsaws, mowers, trimmers, chippers, and trenchers. |
| Heat and cold stress | Working for extended periods of time outdoors in all seasons. |
| Slips, trips, and falls | Working from bucket trucks and working in trees. |
| Motor vehicles and equipment | Working around traffic, motor vehicles, heavy equipment, and overhead hazards. |
| Sharp and/or rotating blades, flying debris | Working around rotating blades, chippers, shredders, trimmers, chainsaws, and mowers. |
| Pesticides and chemical exposure | Working with pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers, gasoline, and batteries. |
| Trenching and excavations | Evaluating soil conditions, verifying utility locations, constructing protective systems, and providing safe access/egress. |
A proactive safety and health program is essential to prevent worker injuries and illnesses in this multifaceted industry. Depending on the activities involved, landscaping and horticultural work may fall under OSHA’s Safety Standards for General Industry and Construction. Training can prove challenging due to the broad range of topics that need to be covered to protect landscaping and grounds crews. Nonetheless, training workers on safety best practices in a way that is consistent with the workers’ literacy and language skills is essential to provide a safe work environment.
Lawn and Landscape Maintenance
This includes tasks such as mowing, pruning, chipping, fertilizing, leaf blowing, pest control, and providing safe transport for the crew to and from the job site. The table below provides information on common injuries related to lawn and landscape maintenance work and how to prevent them.
| Common Injuries | Preventions |
| Cuts and amputations | Keep clear of rotating mower and brush-cutting blades. Maintain saws and cutting equipment in serviceable condition. Do not wear loose clothing around chippers. |
| Hand injuries | Wear gloves. |
| Chemical exposure | Read Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and follow precautions. Implement an effective hazard communication program that includes employee training. |
| Eye injury | Wear protective goggles when using blowers, mowers, etc. |
| Hearing loss | Wear ear protection when using power equipment. |
| Sprains and strains | Maintain comfortable mower settings for workers. Use safe-lifting techniques. Use mechanical means or ask for assistance to lift heavy objects. |
| Vehicle accidents | Train drivers and maintain vehicles in serviceable condition. Train drivers to watch for pedestrians and vehicular traffic. |
Tree Care
Tree care includes activities such as pruning, chipping and removal, plant health care, cabling, bracing, transplanting, and fertilizing. Many hazards in the tree care industry can be fatal. Exposure to overhead power lines, falling branches and tools, and chainsaw use are just a few of the dangers. The table below provides information on common tree care-related injuries and how to prevent them.
| Common Injuries | Preventions |
| Struck by falling debris, cars, etc. | Use personal protective equipment (PPE), implement traffic control safety procedures, and know the drop zone. |
| Lightning | Seek shelter at the first sign of a thunderstorm; have a trained arborist evaluate a damaged tree’s condition before working on a tree that has been struck by lightning. |
| Cuts and amputations | Train workers on safe chainsaw use, and wear chaps. |
| Eye damage | Wear safety goggles. |
| Ear damage | Wear ear protection when using chippers, chainsaws, and other power equipment. |
| Electrocution | Comply with the 10-foot power line clearance rule (10 feet + 4 inches for every 10 kV over 50 kV). |
| Slips, trips, and falls | Use proper PPE and appropriate tie-ins (in tree, bucket, or aerial platform). |